Coronary Angiography and Angioplasty
- What is meant by coronary angiogram?
- Why do I need this test?
- What preparation is required before angiography?
- What steps are followed during the procedure?
- What to expect after the test?
- What is coronary angioplasty ?
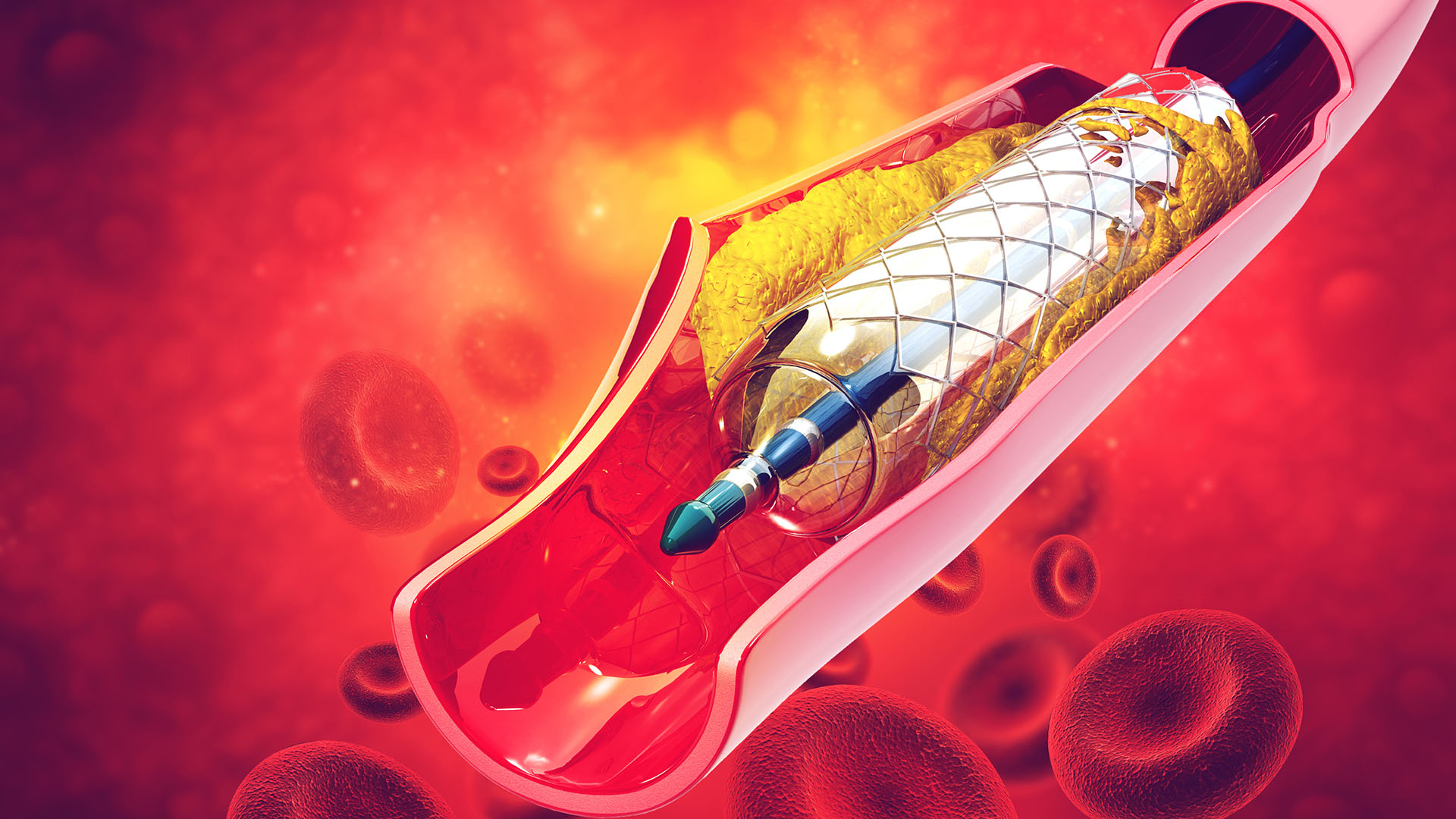
- What is a stent ?
- What are the complications that can happen during angioplasty?
- What are complications that can happen with a stent?
- What is primary angioplasty?
- What is thrombus suction or aspiration?
A special X-ray test, which detects the location and extent of the blockage or narrowing of the coronary arteries is coronary angiogram. The report of this diagnostic test helps to take a treatment call as in, whether the condition can be cured only by lifestyle management, medications or is there a need for any further invasive procedures such as angioplasty or stent, coronary artery bypass surgery (CABG).
This test is needed if you have
- Symptoms of Coronary artery disease (CAD) like chest pain, breathlessness or syncope.
- Stress test, Stress thallium or technetium or Dobutamine stress echocardiogram showing positive test.
- To confirm findings of CT coronary angiogram
- In case of acute heart attack or acute coronary syndrome to confirm and treat the blockages.
- Specific tests which include ECG, 2D echocardiogram, renal function test.
- A fasting period of 4 hours before the procedure.
- Admission of patient (short period wherein the patient is discharged soon, after 2 hours of the test).
The procedure takes 5 minutes. Following steps are carried out:
- A spot on your groin or arm (inside the elbow or wrist) is numbed with local anaesthesiaand then a catheter or a long thin tube is inserted in the artery around it and moved towards the heart. (The pain experienced would be lesser than with any blood test).
- To check for blocked arteries and the structural state of the heart, X-ray monitoring (Angiogram) is carried out after a special fluid (dye- due to which the arteries are shown up well on the X-ray) is injected and reaches the arteries.
- You may be advised to hold your breath during the procedure for a few seconds.
- After this procedure the dye inserted is excreted in urine once the process is complete.
-
- Removal of catheter.
- Application of pressure where the catheter was inserted for 15minutes or longer to avoid internal bleeding.
- Sometimes soreness from lying on your back or where the catheter was inserted.
Throughout your stay with us for this procedure our experienced and pleasant doctor andhis team will be at your service guiding you and answering your every query. Please feel free to ask all your doubts to our consultant cardiologist before the procedure.
-
- Similar to angiography a spot on your groin or arm (inside the elbow or wrist) is numbed with local anaesthesiaand then a catheter or a long thin tube is inserted in the artery around it and moved towards the heart.
- The tube is inserted into the opening of the artery supplying the heart
- A coronary wire which is thinner than your hair( 0.014”)is then passed across the blockage
- Over this wire a balloon is inserted across the blockage. Once the balloon is across the blockage it is inflated from outside to open up the blockage.
- Finally a stent mounted on a balloon is inserted across the blockage and inflated to open up the artery. The balloon is then defalted and removed.
-
A stent is a metal mesh mounted over a balloon. It is made of various materials. Some stents are made of stainless steel others are cobalt chromium or platinum. Its coated with polymer and drug to prevent blockage inside the stent. The drug gradually gets eliminated whereas polymer may or may not get absorbed.
The stent is taken to the site of blockage and the balloon is inflated keep the stent inflated and the balloon is then gradually defalted and taken out. The stent then acts as a scaffold to open up the stenosis. The metal stays in place lifelong inside the body.
-
Some complications which can happen during the angioplasty are artery dissection or tear, artery perforation or hole, arrhythmias (bad fatal rhythms) and even death.
2 major complications that can happen with a stent are stent thrombosis and instent restenosis (ISR)
Stent thrombosis is blockage of the stent due to blood clot. The chances are maximum in first 24 hours. To reduce the complications patient is loaded with 2 blood thinners. Patient usually presents with acute onset chest pain.
ISR is a medium to long term complication. The body reacts to the stent and causes stenosis within the stent. The patient again develops chest pain and breathlessness due to this.
When a patient presents with massive heart attack there are 2 ways to treat.
Thrombolysis (Clot busting injections)
Primary angioplasty .
Primary angioplasty is the best treatment for acute massive heart attack. Its going inside the heart like a routine angioplasty(As mentioned above), removing the clot and placing a stent.
In case of acute severe heart attack if there is a blood clot causing an obstructioin. An alternative way other than a balloon inflation is to take in suction devices inside the heart through a tube from your groin or hand and sucking it out. This helps reestablish flow in the heart and prevent further damage of heart muscles.
- When can I join duty after angiography?
- Is angiography a major surgery?
- Will I be fine after angiography?
The very next day if the angiogram doesn’t show significant coronary artery disease.
No it is not considered as a major surgery.Its classified as minimally invasive diagnostic procedure.
Angio in Latin means vessels , So a graph or image of the vessel is angiography. It’s a test just like a CT scan or MRI it is not a therapy. After the angiogram the cardiology ascertains whether to keep the patient on medical management, do and angioplasty or send for bypass surgery to the surgeon.
In short an angiogram is a test to detect the narrowing of arteries supplying the heart,whereas angioplasty is a procedure to expand these arteries.
At Care For Your Heart we provide comprehensive cardiac treatment to all our patients.
“Do your part, Care for your Heart“
“Do your part, Care for your Heart“
© Behearthealthy 2023. All rights reserved. Site Designed by U1R
