Be Heart Healthy, led by Dr. Ankur Phatarpekar, stands as a beacon of cardiac care excellence in Dadar. Renowned as the best cardiologist in Dadar, Dr. Phatarpekar combines exceptional skill with a compassionate approach, ensuring each patient receives personalized care. Specializing in the treatment of coronary artery disease (CAD), Dr. Phatarpekar’s clinic offers cutting-edge interventions like TAVI, TMVR, and MitraClip procedures, ensuring the highest standards of care. By choosing Be Heart Healthy, patients gain access to advanced cardiac care delivered with empathy and expertise. Don’t wait to address your heart health. Schedule a consultation with the best cardiologist in Dadar today and take the first step towards a healthier heart.
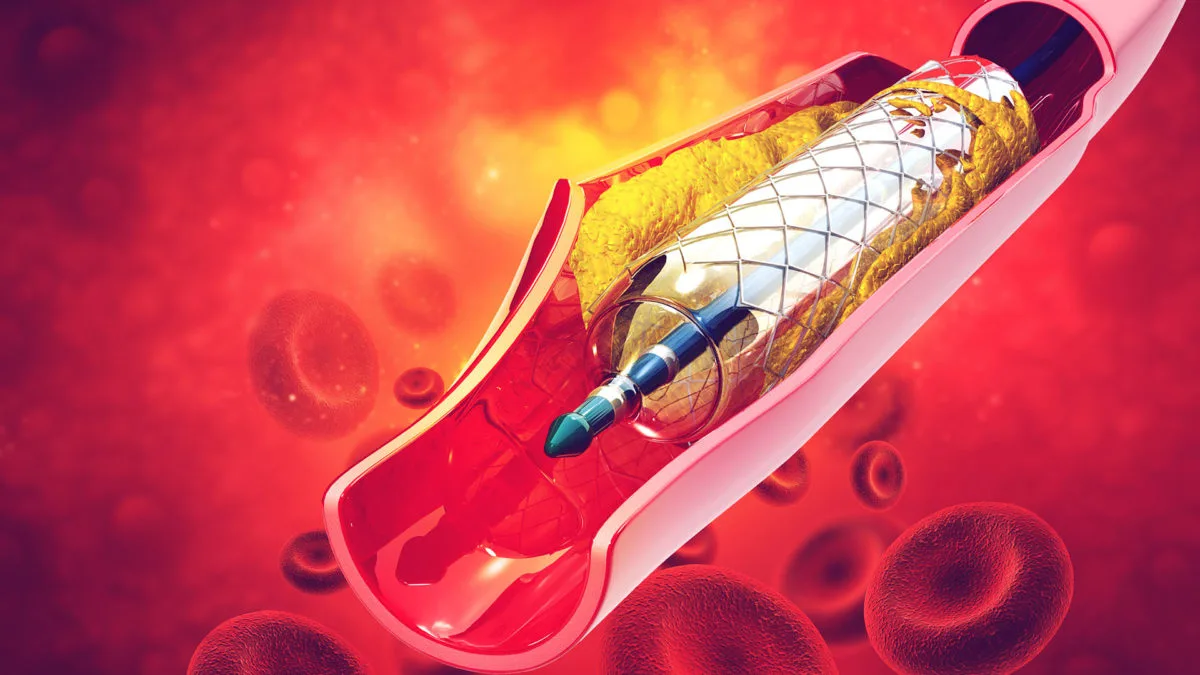
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) also known as Ischemic Heart Disease is one of the leading causes of 7 million deaths across the globe targeting 7% of the urban population and 3.1% of the rural population in India.


With a strong commitment to staying at the forefront of cardiovascular medicine, Dr. Ankur regularly participates in training programs and Proctors other cardiologists in the latest techniques. His dedication to advancing the field of interventional cardiology and providing the highest standard of care makes him the top choice for patients seeking the best cardiologist in Mumbai.
For residents of Navi Mumbai seeking the best heart hospital in Mumbai, look no further than Be Heart Healthy, led by Dr. Ankur Phatarpekar. With a reputation for excellence and a commitment to providing the highest quality care, Be Heart Healthy is the premier destination for comprehensive cardiac care in Navi Mumbai.
As a leading heart specialist in Navi Mumbai, Dr. Ankur specialises in a range of advanced procedures, including TAVI, MitraClip, BMV, and other interventional cardiology techniques. His expertise and dedication to patient care have earned him a reputation as one of the top cardiologists in Mumbai, with patients travelling from across the country to seek his services.
At Be Heart Healthy, we understand the importance of early detection and prevention of heart disease. That’s why we offer comprehensive screening and diagnostic services to help identify risk factors and develop personalised treatment plans. Our team of experienced professionals is committed to providing compassionate care and support to help you achieve optimal heart health.
Whether you’re seeking treatment for a specific cardiac condition or looking to improve your overall heart health, Be Heart Healthy is here to help. Trust us to provide the expert care and support you need to live a heart-healthy life.
Structural heart & pediatric heart diseases: The heart is the most important organ in the body which receives deoxygenated or impure blood from different parts of the body. This blood is then transported to the lungs for purification and the oxygenated or purified blood is then pumped by the heart to the rest of the body.
Call us now if you are in a medical emergency.