Did you know that around 600,000 sudden cardiac deaths are reported annually in India, and around 300,000 cardiac deaths in the USA?
Moreover, the overwhelming part is that at least 200,000 deaths each year from heart disease are preventable but occur because of negligence. If sudden cardiac death is not immediately treated, it can cause the patient’s death.
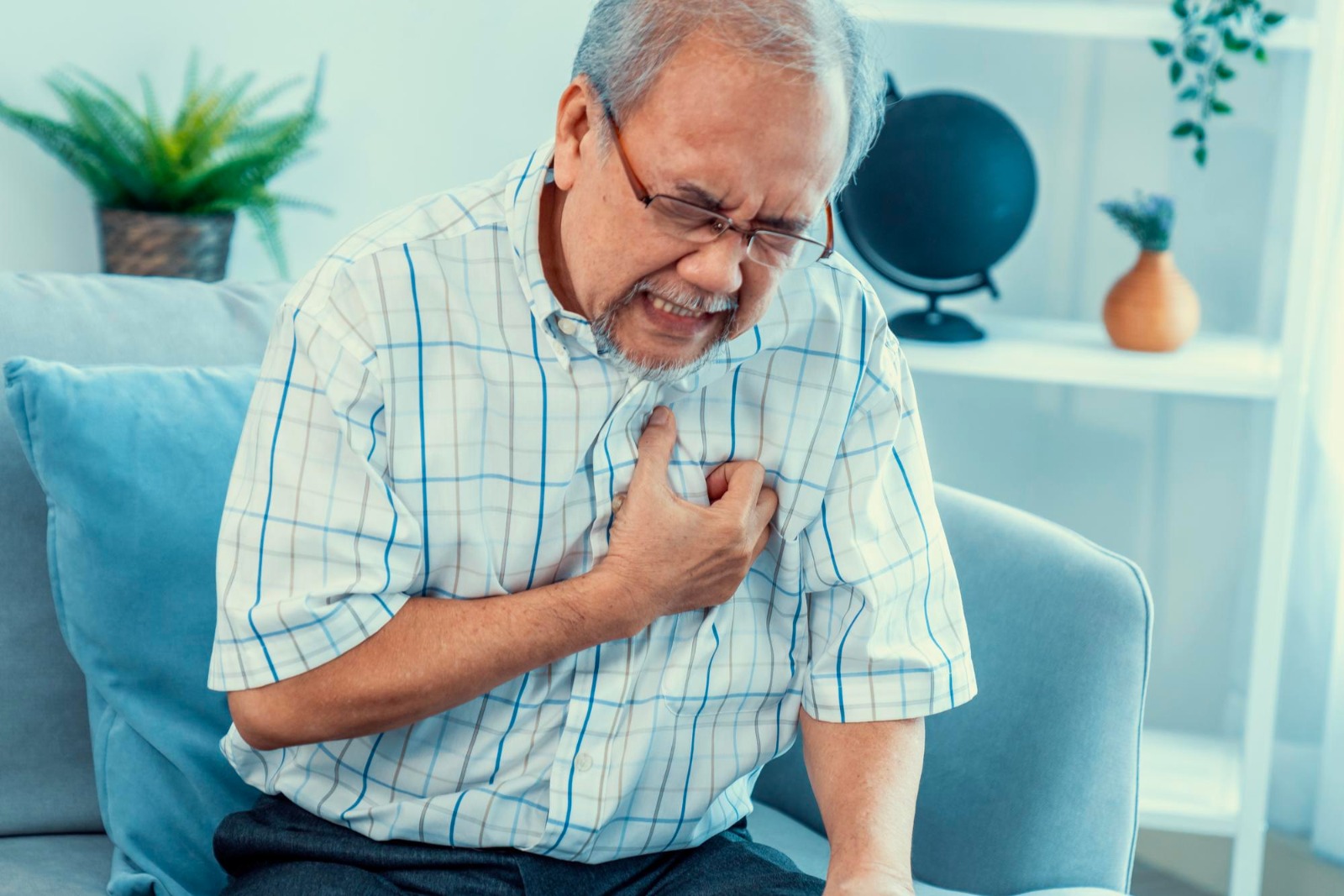
Sudden cardiac death, also known as SCD, is the unexpected stoppage or obstruction of the heartbeat, which inhibits the blood flow to the body's vital organs, such as the brain, leading to unconsciousness. It is common in people who previously encountered any heart attack or cardiac disease but can also occur in healthy individuals.
Lifestyle factors such as obesity, smoking, diet, high blood pressure, and cholesterol play a major role in causing sudden cardiac deaths and heart diseases. In this article, we will discuss everything about sudden cardiac death, its symptoms, causes, risk factors, and how to prevent it.
What Is Sudden Cardiac Death?
Sudden cardiac death is an unexpected inhibition of the heart functioning due to any underlying cardiac issue like coronary artery disease.
Sudden cardiac death occurs within a short period of time, generally less than 1 hour from the occurrence of symptoms. SCD is often used interchangeably with sudden cardiac arrest, the unexpected cessation of the heartbeat.
Diagnosis
The confirmation of the diagnosis of sudden cardiac death is commonly made through radiological instruments, like MRI, CT scan, or electrocardiogram, an instrument used to measure the heart’s structure or electrical activity.
A doctor may conduct diagnostic tests to monitor the activity of the patient’s heart if they are at high risk for SCD to prevent the disease.
The tests used to diagnose sudden cardiac death include:
- ECG or electrocardiogram
- Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- Blood tests to identify electrolyte imbalances
- Cardiac catheterization
Causes Of Sudden Cardiac Death
The most common cause, and up to 80% of all cases of sudden cardiac death, is coronary artery disease, which is the blockage of the coronary artery that supplies blood to the heart due to plaque buildup. Other causes of sudden cardiac death include:
- Obesity
- Fibrosis
- Alcoholism
- Ischemic heart diseases
- Heart valve disease, such as mitral valve regurgitation.
- Cardiomyopathy or enlarged heart
- Congenital heart defect (heart problems present by birth).
- Untreated hypertension
- Diabetes
- Sudden emotional stress
- History of other heart problems
Symptoms Of Sudden Cardiac Death
Sudden cardiac death can be symptomatic ( occurring with symptoms) and asymptomatic ( occurring without symptoms), varying from patient to patient. Sudden cardiac death may include one or more of the following symptoms:
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Shortness of breath
- Dizziness
- Fainting or close to fainting (loss of consciousness).
- Rapid or irregular heartbeats
- Unexplained wheezing
Risk Factors
Sudden cardiac death shares many common risk factors and causes. The major risk factors of sudden cardiac death include:
- Smoking
- Dyslipidemia (The imbalance of lipids in your body, such as cholesterol, triglycerides, HDL, and LDL).
- Family history of heart disease or premature coronary artery disease.
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Diabetes and hypertension
- Obesity
- Chronic kidney disease
- SCD is more common in males
- The use of illegal drugs, such as amphetamine or cocaine
How To Prevent Sudden Cardiac Death?
To prevent sudden cardiac death, there are two protocols:
- Treating the underlying cause, such as heart disease or other factors increasing the risk of sudden cardiac death.
- Lifestyle and dietary modifications
Treating Underlying Cause
As we discussed, the most common cause of sudden cardiac death is heart disease or any
previous history of cardiac disorder, such as coronary artery disease (CAD), myocardial
ischemic disorder, or heart valve disease.
- For cardiac diseases, coronary artery disease or heart valve disorder, surgical treatments, such as angioplasty, MitraClip therapy, or placement of Impella heart pump device for assisted angioplasty are done to restore normal blood flow to the heart and the rest of the body.
- The use of pacemakers or implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICDs) is placed in the chest to detect and stop irregular heartbeats, preventing sudden cardiac death.
Lifestyle And Dietary Modifications
The second protocol, also known as primary prevention of SCD, is followed alone or in
combination with surgical treatments, which includes lifestyle and dietary modifications.
-
- For obese individuals, maintaining a healthy weight is a must to prevent SCD.
- Controlling blood pressure, cholesterol, and blood sugar levels.
- Regular checkups
- Screening yourself periodically for any potential heart diseases.
- Exercise
- Quitting smoke and tobacco or illicit drug use
.