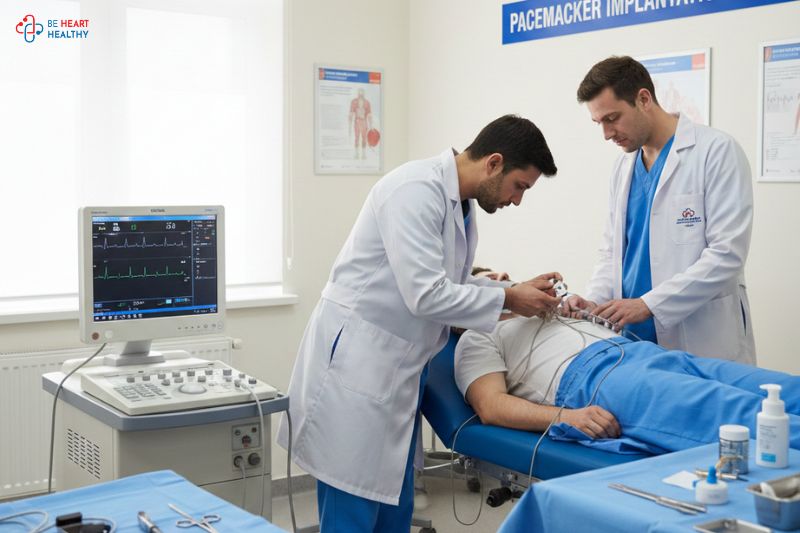
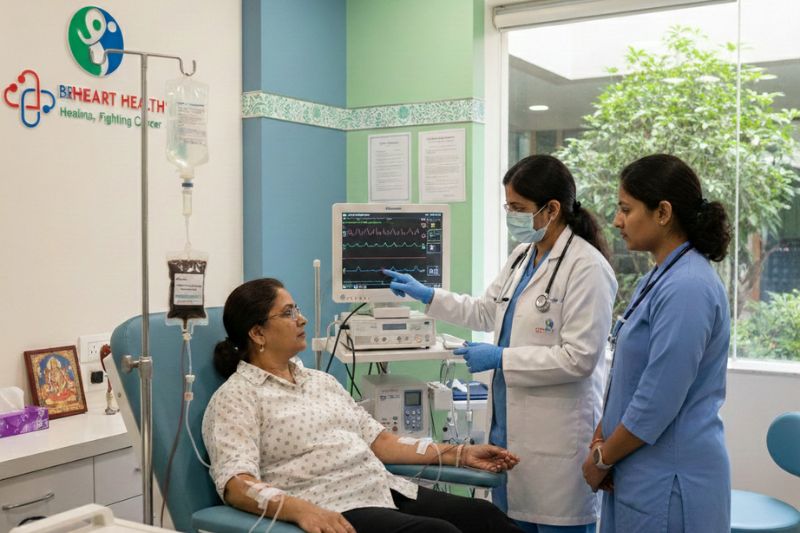A computerized tomography (CT) coronary angiogram is an imaging technique used to assess the condition of arteries supplying the heart, known as coronary arteries. A powerful X-ray machine is used to produce images of coronary arteries and the heart. This investigation is used to diagnose various conditions affecting the heart and coronary arteries. It can help to determine if a plaque is being build-up in a coronary artery that has led to the narrowing of the arteries. Blood flow distal to the plaque can be assessed by CT angiogram because it can reduce or in some cases completely obstruct the blood flow in the affected coronary arteries. For information regarding plaque formation and thrombosis, visit our facebook page.
In the patient undergoing CT angiography, the intravenous contrast material can be used that can help to produce clear images of the coronary arteries. Images generated from the CT angiography can be two-dimensional or three-dimensional and can be reformatted in multiple planes. These images can be saved using various devices like CD or DVD and can be watched again by your doctor if required. (1)
Uses of CT Coronary Angiography:
Doctors can use this technique for diagnosing and assessing the severity of various conditions affecting the heart and vessels. The most common conditions are described below:
- Anatomical abnormalities of coronary arteries.
- Patients with chest pain and associated with unclear investigation results such as ECG. These patients are at low to moderate risk of coronary artery disease, so CT angiography can be done.
- Atypical chest pain in the emergency department raises concern for CT angiography.
- Heart failure with reduced ejection fraction on echocardiography with low-intermediate risk of coronary artery disease.
- Medium risk of coronary artery disease with a history of surgery not involving the heart or coronary arteries.
- Before coronary artery bypass grafting
- Unclear stress test results
The patients fulfilling the above criteria should undergo CT angiography which can help to provide various information other than the formation and extent of plaque in the coronary arteries. Other information that can be determined from CT angiography includes aortic abnormalities, clot formation leading to pulmonary circulation (related to lungs), and collapsed lungs. The plan for CT coronary angiography will be decided by your physician or cardiac specialist.

Preparation Before the Test:
Before a visit for CT coronary angiography, your cardiologist will advise some instructions that are essential in preparation for CT angiography. These include the following:
Food and Medications
Before the CT angiography test, you need to be fasting for at least 4 hours for food items however, you can drink fluids before the test. Avoid caffeinated drinks for at least 12 hours before performing CT angiography because they can increase the heartbeat and it will be difficult to take clear images.
Your medical consultant should know all the medications you are taking and you may need to miss doses of some medications before the test.
Avoid Metals items and Jewelry
No metal should be worn while performing the test. You will need to remove your jewelry, clothing, etc. before the test. You will be asked to wear a gown before the test.
References:
- Sun Z, Sabarudin A. Coronary CT angiography: State of the art. World J Cardiol. 2013 Dec 26;5(12):442–3.
- Kumamaru KK, Hoppel BE, Mather RT, Rybicki FJ. CT angiography: current technology and clinical use. Radiol Clin North Am. 2010 Mar;48(2):213–35, vii.